7 Hidden Ecommerce SEO Mistakes Stores Must Avoid
For ecommerce stores, SEO is not something that can be overlooked. Sites with good SEO that rank on the first page of Google (with target keywords) earn at least 75 percent of all search traffic. Because SEO is so important, this post will explore the top seven SEO mistakes ecommerce stores must avoid if they want their pages to rank highly in search.
SEO allows you to drive hundreds, if not thousands, of visitors to your store for “free” every day. Being ranked at the top of search results can not only improve site traffic but also increase conversions. However, there’s a catch: a lot of the time, the first page of search results is dominated by big-name brands with high domain authority (DA).
Giants like Amazon and eBay have done a great job at acquiring customer trust. However, the sheer size and wide variation of their product offerings can be seen as a disadvantage from an SEO perspective.
If your store follows SEO best practices and focuses on building a strong brand presence in your niche, there’s no reason your brand can’t make its way to the front page (if not the first spot) in search rankings.
Below are the biggest SEO mistakes that ecommerce business owners make and what you should be doing to improve your SEO strategy. Heeding this advice will hopefully lead to more site visitors and an increase in sales on your ecommerce website. Let’s dive right in.
SEO mistakes your ecommerce store needs to avoid
1. Having multiple sitemaps
As an ecommerce site, it can be difficult with all of those product offerings to keep it all squeezed into a single sitemap.
When people visit your site, they use internal links—those found in the top navigation, footer, and other places where you have linked items—to find their way around.
Sitemaps show the structure of your website—telling search engine bots how many pages you have and how they are connected. It is the tool search engines use to index every page on your store, even if you haven’t been strategic yet with internal linking.
However, this is hard to do and can get complicated when you have the issue of multiple sitemaps. Having multiple sitemaps can confuse search engines and can prevent them from indexing your pages properly.
If your ecommerce store contains over 50,000 URLS, multiple sitemaps are a good idea, but brands must be conscious of how to submit their sitemaps to search engines. Google provides good instructions on how to do this.
It’s recommended best practice to resubmit your sitemaps to the appropriate search engines whenever making changes to your website, or creating new pages you want to have appeared in search results. This helps reduce the time it takes for search engines to crawl your site and decide where your content ranks.
WooCommerce has recommendations on what ecommerce stores can do when they have multiple sitemaps and want to ensure their products appear in search results.
2. Not making your site mobile friendly
Google, the world’s largest search engine, is particularly shrewd with the details as to how they choose to rank sites. Plus, the Google search algorithm gets consistent updates made to it, making it all the more important for brands to pay attention when changes happen.
Mobile-friendliness and responsive website design are no exception. In fact, it’s been a core component of the Google ranking algorithm since 2015.
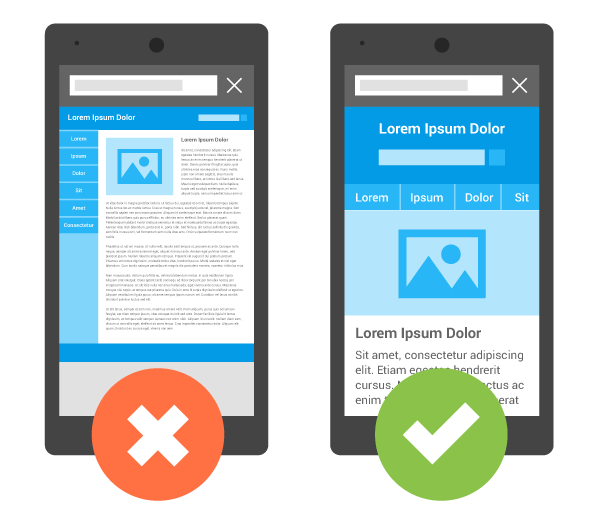
Since then, Google has made repeated updates on the algorithm and how it evaluates mobile responsiveness. In September 2020, they switched over to mobile-first indexing. Meaning, they now index the mobile version of your website first, encouraging website owners to prioritize the look and feel of their mobile site before desktop or tablets.
For ecommerce, mobile optimization is especially important. According to one study, shopping cart abandonment rates were as high as 80 percent on mobile compared to 73 percent on desktop.
Why such a difference?
It’s because people still approach web development from a desktop-first perspective, even though more searches now happen on mobile than on desktop. To help make your ecommerce store mobile-friendly, follow these tips:
Perform a site audit
There are some great tools out there that will quickly identify issues with your mobile website. Your first port of call should be Google’s very own Mobile-Friendly Test. Simply paste in a URL and it will give you a clear idea of whether or not that page is mobile-friendly. If there are any issues, they will be listed out in the results.
For a more precise look at issues, you should check out BrowserStack. This handy tool lets you see how your website appears on several device types across different browsers. It’s a useful way to pinpoint and tweak minor issues that arise.
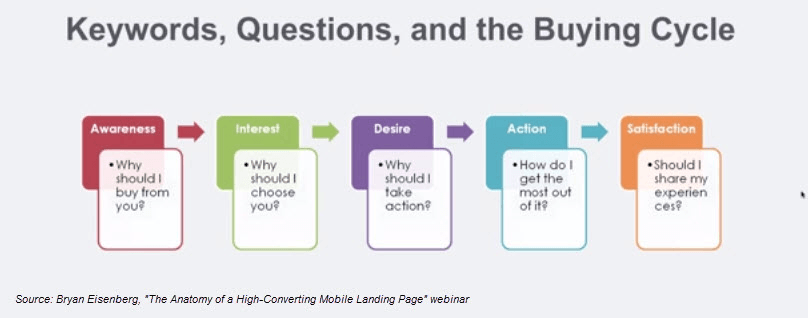
Consider the buyer’s cycle
ecommerce stores should regularly evaluate their omnichannel touchpoints—cleaning up those pages and posts that have become irrelevant to the buying cycle. As outlined in the image below, a typical consumer goes through a five-stage process when buying anything from an ecommerce store.
If you have information on your product pages that does not benefit the buyer, then it’s time to reevaluate, optimize, and potentially remove them.
For example, maybe some of your product pages are overwhelming the customer with too much text and poor UX/UI design. For this, many brands choose to use an “accordion” layout on mobile devices.
Take a look at this example below from Hustler Ethos’ mobile site:

In this instance, the buyer knows what stage comes next, but sections only load as they need to see them.
ecommerce brands can also improve conversion rates by implementing user-generated content into their website and product pages.
Remove distractions
Google has outlined that any elements making a mobile webpage less interactive and harder to navigate should be removed. This includes things like:
- Full-page pop-ups that are hard (or impossible) to close
- Sidebars
- Links that are too small to click
- Elements that require the page to scroll horizontally
Include clear calls-to-action (CTAs)
Ensure that CTA buttons, like “Buy Now” or “Add to Basket”, are easy to find and click on. This is especially important on large product pages that require customers to do a lot of scrolling.
You may want to make these buttons “sticky” at the bottom of the page. That way, as soon as the customer is ready to take any action the button is right there.
3. Slow site speed
Site speed is critical for SEO success in the ecommerce industry. It’s common sense, as people want information and they want it now.
Internet users are increasingly impatient, as they have many websites to shop from that have fast page speed. If people feel your site isn’t loading quickly enough, they will simply find another ecommerce store to shop at.
Google itself supports this notion, recommending that no page should take longer than three seconds to load. Studies have shown that bounce rate (the percentage of visitors that leave without interacting with a page) increases as site speed gets worse.
So, how do you improve ecommerce site speed?
- Upgrade your hosting: Premium web servers will load your website far more quickly than cheap ones. Good hosting may not be cheap, but it is well worth the investment to see positive search results.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN is a massive distribution of servers around the world. They enable your website to load from different servers depending on where the user is located, thus enabling faster page load times.
- Optimize all images: ecommerce sites are, by nature, very image-heavy. Unfortunately, this can put a ding in website page speed. Make sure any images and videos are compressed and optimized for the web and search.
- Remove unnecessary plugins: With so many plugins available for the backend of websites, it can be easy to lose track of how many you have. The problem is, too many plugins can contribute to slow page speed. While it may sound counterintuitive, there’s a plugin that can help you monitor your plugins! It’s called P3 and performs scans of all plugins on your site, telling you which ones are having the biggest impact on overall page load speeds.
- Clean up your redirects: If your store is several years old, you may have a lot of redirects in place on your ecommerce store. Worse still, you could even have “redirect chains” which take the visitor to multiple pages before finally getting a link they can interact with (if they don’t bounce before that). This has a massive impact on both site speed and SEO as the server has to reload each time it goes to a new URL.
4. Keyword-stuffing and thin pages
There are two big issues common with how inexperienced store owners approach their product pages.
1. Pages stuffed with keywords with no quality content
2. Pages with hardly any content at all
Why is this an issue? Let’s look at each one:
1. Keyword stuffing
“Men’s size 8 sports trainers for sale!
Looking to buy a brand new pair of men’s size 8 sports trainers? No problem! We have the biggest range of men’s size 8 sports trainers anywhere online. With our men’s size 8 sports trainers, you will wonder how you ever lived without them. Check out our range of men’s size 8 sports trainers below and buy a pair today!”
From Google’s perspective, the description above is considered spammy—containing the focus keyword multiple times without much meat to it. Doing this hurts your SEO efforts rather than benefiting them. In the 2000s and early 2010s, this strategy of keyword stuffing may have had success, but the Google algorithm is too advanced for this now.
Plus, on a simple human level, who would read that and be impressed anyway?
Moving forward, be sure to use keywords sparingly throughout your page copy. It is perfectly acceptable to include them in page titles, meta descriptions and headings, but be sure to do so in a way that does not look insincere. Instead, opt for a range of similar keyword variations.
When working to produce high-quality data-driven content, it may be useful to try a tool like RankTracker. It helps you write content that appeals both to real people and search engines.
2. Thin pages
Here’s an example of what a “thin page” may look like:
Men’s size 8 sports trainers
Product details:
- Size 8
- For men
*Free delivery
Consider a product page that contains little more than what is written above. How well do you think this will perform with search engines?
The answer is not very well. When a user lands on the page, it doesn’t offer value in the way of trying to convince the buyer to purchase the product.
Similarly, almost 95 percent of online shoppers read reviews before deciding to purchase. These can be hugely beneficial in converting a visitor into a buyer. So try to encourage those customers to come back and leave a review of your product!
This kind of user-generated content will include the types of keywords that search engines use to rank your site, so it’s a win-win.
5. Plagiarizing and duplicating content
Duplicate content has long been recognized as one of the biggest SEO mistakes. It’s naturally a very big problem in the world of ecommerce since product descriptions end up getting copied and pasted to sites like Amazon, Aliexpress, and eBay.
Because search engines have already indexed this content elsewhere, they simply flag it as duplicated on your site. So if anything, it has a negative SEO effect.
Instead, take the time to rewrite your product descriptions to ensure there is novel content on your site. If other stores are taking this copy-and-paste approach, then see it as an opportunity to get ahead.
6. Not having an SSL certificate
An SSL Certificate is a stamp of proof showing that the connection between the server and the user is encrypted. Essentially, this says that your website is safe to use. Websites must have the added ‘s’ after HTTP in their web address. Those that don’t will take a hit to their SEO.

The reason behind this being an important ranking factor is that it ensures a user’s information is safe. If your ecommerce store does not have an SSL Certificate, a buyer’s private information (including credit card number) is more vulnerable to being hacked and stolen. Getting an SSL Certificate can vary depending on your hosting provider, so your first port of call should be to contact them.
7. Not creating a blog for your store
While SEO-optimized product pages are useful for helping products rank over time, a blog can also be an important SEO asset to your ecommerce store. A blog can help further grow your brand visibility and drive larger levels of traffic via backlinks, brand mentions, organic search, and even targeted local SEO traffic.
On a blog, you can write posts that complement the product sold in your online store. For example, for a sportswear brand, it could be worthwhile to create a written guide on “The Best Men’s Sports Trainers For Running.” This post contains a “high intent” keyphrase that the brands can use to link directly to specific products their store offers.
The amount of time and effort you spend on your blog is entirely up to you. However, a regular content marketing strategy coupled with link building is a great way to get ahead of the competition.
AWAY luggage took this one step further and created their own publication, HERE Magazine as a way of encouraging travel and expanding their branding:
Conclusion
If you’ve never paid much attention to ecommerce SEO mistakes, there’s a good chance your site has fallen victim to one or a number of these pitfalls. But luckily, SEO can always be worked on and improved. Even if you have a poor score, that doesn’t mean you can’t turn it around.
Many of these issues are relatively easy to fix, such as gaining an SSL certificate or removing plugins that reduce site speed. Other issues, like redesigning the mobile version of your site and developing a blog will require more time and effort. But remember, SEO has been and always will be a long-term strategy, that’s what makes SEO worthwhile in the first place.
Following these tips and applying them to your ecommerce store is a positive first step in generating higher organic web traffic and, hopefully, more online conversions.